Unsupervised Deep Learning by Neighbourhood Discovery
Accepted by 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'19)
Queen Mary University of London
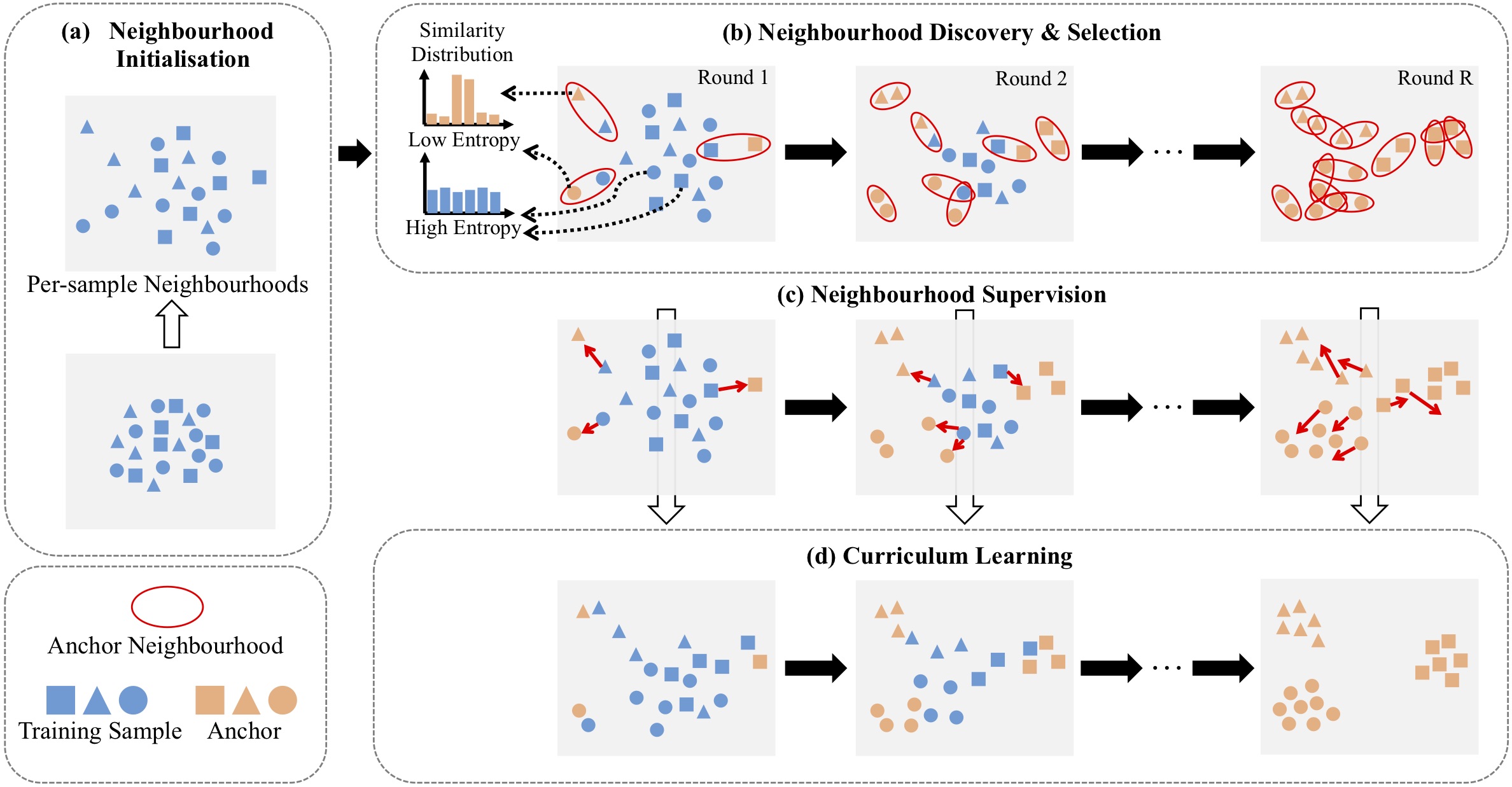
Description
Deep neural networks have significantly advanced the progress of computer vision problems, nevertheless, most of them are heavily relying on massive collection of exhaustively labelled training data. As such, unsupervised learning of deep features has recently drawn increasing attention.
In the literature, representative unsupervised deep learning methods include clustering and sample specificity analysis. Methods fall in the former category has great potential with the best case reaching the performance of supervised learning but is error-prone. In contrast, sample specificity learning treats every single sample as an independent class and hypothesis that the model can reveal the underlying class-to-class semantic similarity structure. However, the ambiguous supervision leads to its weak discriminative ability. Other contemporary methods like self-supervised learning and data synthesis share a similar limitation due to the insufficient correlation between the auxiliary supervision and the underlying class target.
We present a generic unsupervised deep learning method called Anchor Neighbourhood Discovery (AND). With a divide-and-conquer principle, the AND discovers class consistent neighbourhoods anchored to individual training samples (divide) and propagates the local inter-sample class relationships within such neighbourhoods (conquer) for more reliably extracting the latent discrimination information during model training.
We make three contributions:
- We propose the idea of exploiting local neighbourhoods for unsupervised deep learning. To our best knowledge, it is the first attempt at exploring the concept of neighbourhood for end-to-end unsupervised deep learning of visual features.
- We formulate an Anchor Neighbourhood Discovery (AND) approach to progressive unsupervised deep learning.
- We further introduce a curriculum learning algorithm to gradually perform neighbourhood discovery for maximising the class consistency of neighbourhoods therefore enhancing the unsupervised learning capability.
Benchmarks
Extensive experiments are conducted on the following six datasets and the results show the advantages of our AND method over a wide variety of existing state-of-the-art unsupervised deep learning models.
- CIFAR10(/100): An image dataset with 50,000/10,000 train/test images from 10 (/100) object classes.Each class has 6,000 (/600) images with size \(32\!\times\!32\).
- SVHN: A Street View House Numbers dataset including 10 classes of digit images.
- ImageNet: A large 1,000 classes object dataset with 1.2 million images for training and 50,000 for test.
- CUB200-2011: A fine-grained dataset containing 5,994/5,794 train/test images of 200 bird species.
- Stanford Dogs: A fine-grained dataset with 12,000/8,580 train/test images of 120 dog breeds.
Please kindly refer to the paper for more details and feel free to reach me for any question.